Difference between revisions of "Maple/Phasors"
(→Reporting Single Complex Number in Polar Form) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===Converting to rectangular coordinates=== | ===Converting to rectangular coordinates=== | ||
Use the <code>evalc(NUM)</code> command to convert to rectangular coordinates. | Use the <code>evalc(NUM)</code> command to convert to rectangular coordinates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Calculating Parallel Impedances === | ||
| + | The following processes will calculate a numerical or symbolic value for some set of parallel impedances; PAR is for two items while the more complicated PARn can be used for two or more: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=maple> | ||
| + | PAR := (Za, Zb) -> simplify(Zb*Za/(Za + Zb)) | ||
| + | PARn := proc () simplify(1/convert(map(proc (x) 1/x end proc, [args]), `+`)) end proc | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===Simplifying solutions=== | ===Simplifying solutions=== | ||
Solutions involving the <code>polar</code> command must first be evaluated using the <code>evalc</code> command before using the <code>simplify</code> command. | Solutions involving the <code>polar</code> command must first be evaluated using the <code>evalc</code> command before using the <code>simplify</code> command. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Reporting Single Complex Number in Polar Form === | ||
| + | The following process will display the magnitude and phase angle (in degrees) of a complex number; note that it relies on the argumentd function above: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=maple> | ||
| + | printphasor := N -> printf("%0.3e < %0.3e", abs(evalc(N)), argumentd(evalc(N))) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Reporting Phasors Solution List as Magnitudes and Angles in Degrees=== | ||
| + | Maple can be asked to process a list of results to report them as phasors. The '''listphasors''' command takes an input argument that comes from the solve command and prints the results as a table of variables, magnitudes, and angles in degrees. The command is given below in the next section. | ||
==Handy commands== | ==Handy commands== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 48: | ||
polard:=(mag, angd)->polar(mag, angd*Pi/180); | polard:=(mag, angd)->polar(mag, angd*Pi/180); | ||
argumentd:=(num)->argument(num)*180/Pi; | argumentd:=(num)->argument(num)*180/Pi; | ||
| + | listphasors := proc (plist) local k; for k to nops(plist[]) do printf("%s = %f < %f deg\n", lhs(plist[][k]), abs(evalc(rhs(plist[][k]))), argumentd(evalc(rhs(plist[][k])))) end do end proc | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (whee!) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples == | ||
| + | The following are PDFs of the Maple worksheet used to solve the problems listed. | ||
| + | * Alexander & Sadiku Practice Problem 10.1 (single frequency) [http://pundit.pratt.duke.edu/piki/images/7/78/PracProb10p01.pdf PDF] <!-- File: [[File:PracProb10p01.pdf]] --> | ||
| + | * Alexander & Sadiku Example Problem 10.6 (three frequencies) [http://pundit.pratt.duke.edu/piki/images/a/a2/ExProb10p06.pdf PDF] <!-- [[File:ExProb10p06.pdf]]--> | ||
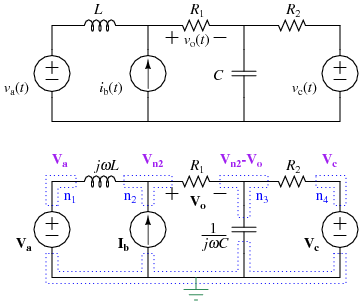
| + | ** The worksheet uses following labels (adapted from '''Fundamentals of Electric Circuits,''' Charles Alexander & Matthew Sadiku, 5th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2013) | ||
| + | <center>[[File:ASExProb10p6.png]]</center> | ||
| + | * Svoboda & Dorf Example 10.8-1 (two frequencies) [http://pundit.pratt.duke.edu/piki/images/a/a3/ExProb10p08d01.pdf PDF] | ||
[[Category:ECE 110]] | [[Category:ECE 110]] | ||
[[Category:EGR 224]] | [[Category:EGR 224]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:31, 20 March 2022
This page contains handy Maple functions for use with Phasors and Phasor analysis.
Contents
- 1 Processes
- 1.1 Entering a numerical value for phasor or complex number
- 1.2 Obtaining magnitude and phase values
- 1.3 Converting to rectangular coordinates
- 1.4 Calculating Parallel Impedances
- 1.5 Simplifying solutions
- 1.6 Reporting Single Complex Number in Polar Form
- 1.7 Reporting Phasors Solution List as Magnitudes and Angles in Degrees
- 2 Handy commands
- 3 Examples
Processes
Entering a numerical value for phasor or complex number
To enter a complex number in rectangular coordinates, use \(I\) (capital I) as the imaginary number or else re-define the variable \(j\) as the imaginary number with
j:=I
at the start of your code.
For polar representations, you can use the polar(MAG, ANG) command. Keep in mind that the angle will need to be in radians. If you want to be able to use polar coordinates with degrees, you can define a new version of polar as follows:
polard:=(mag, angd)->polar(mag, angd*Pi/180)
Obtaining magnitude and phase values
To get the magnitude of a complex number, use the abs command. To get the angle, use argument but keep in mind the angle will be in radians. To get the angle in degrees, either multiple the output from argument by 180/Pi or create a new argumentd function for yourself:
argumentd:=(num)->argument(num)*180/Pi
Converting to rectangular coordinates
Use the evalc(NUM) command to convert to rectangular coordinates.
Calculating Parallel Impedances
The following processes will calculate a numerical or symbolic value for some set of parallel impedances; PAR is for two items while the more complicated PARn can be used for two or more:
PAR := (Za, Zb) -> simplify(Zb*Za/(Za + Zb))
PARn := proc () simplify(1/convert(map(proc (x) 1/x end proc, [args]), `+`)) end procSimplifying solutions
Solutions involving the polar command must first be evaluated using the evalc command before using the simplify command.
Reporting Single Complex Number in Polar Form
The following process will display the magnitude and phase angle (in degrees) of a complex number; note that it relies on the argumentd function above:
printphasor := N -> printf("%0.3e < %0.3e", abs(evalc(N)), argumentd(evalc(N)))Reporting Phasors Solution List as Magnitudes and Angles in Degrees
Maple can be asked to process a list of results to report them as phasors. The listphasors command takes an input argument that comes from the solve command and prints the results as a table of variables, magnitudes, and angles in degrees. The command is given below in the next section.
Handy commands
Given the above, here is a list of the handy commands that can be copied into the beginnings of a Maple worksheet:
j:=I;
polard:=(mag, angd)->polar(mag, angd*Pi/180);
argumentd:=(num)->argument(num)*180/Pi;
listphasors := proc (plist) local k; for k to nops(plist[]) do printf("%s = %f < %f deg\n", lhs(plist[][k]), abs(evalc(rhs(plist[][k]))), argumentd(evalc(rhs(plist[][k])))) end do end proc
(whee!)
Examples
The following are PDFs of the Maple worksheet used to solve the problems listed.
- Alexander & Sadiku Practice Problem 10.1 (single frequency) PDF
- Alexander & Sadiku Example Problem 10.6 (three frequencies) PDF
- The worksheet uses following labels (adapted from Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, Charles Alexander & Matthew Sadiku, 5th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2013)
- Svoboda & Dorf Example 10.8-1 (two frequencies) PDF